The path element
In this lesson, we'll dive into one of the most versatile and powerful elements in SVG: the <path> element.
The <path> element allows you to create complex shapes and lines that go beyond the basic geometric shapes. It is essential to build some graph types like an area chart or a line chart.
Most basic example
The <path> element allows to draw literally any shape in the SVG area.
You provide it with a series of drawing commands that will make straight or curved lines, resulting in your final shape.
Let's check a basic example:
<svg height="300" width="400">
<path
d="M0 105 L100 200 L200 200 L300 20 L350 120"
fill="none"
stroke="#69b3a2"
/>
</svg>This will result in the following shape:
Nice! This almost look like a line chart already!
As you can see the <path> element expect a required d attribute. This attribute defines the shape of the path. Let's discover its syntax.
Understanding the d Attribute
The d attribute defines the shape and outline of the path by specifying a series of drawing commands.
Each command consists of a letter that represents the type of drawing action (such as M for Move To) followed by one or more numbers that define the coordinates or control points.
Here is a breakdown of the svg path above:
Remember that the coordinate system starts from the top left in svg!
M0 105: moves the starting point of the path to coordinates0, 105. (Mstands for move to)L100 200: draws a straight line from the current point (0, 105) to the point (100, 200). (Lstands for line to)200 200: draws a new straight line from the current point to the point (200, 200).
Now, experiment with some changes in the sandbox below to get a better understanding of how it works:
Not only lines!
The path element can create a wide variety of shapes, including the most complex ones.
Two particularly useful features are the Bézier curve (C) and the arc curve (A). Check how they work with those 2 diagrams:
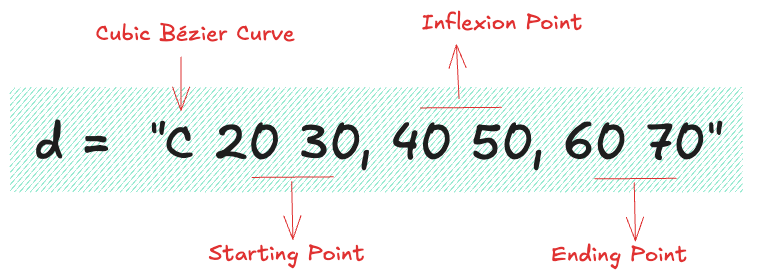
Ok, that's definitely not easy to grasp.
In the sandbox below, try to play with the numbers, and see what happens.
Exercises
The good news 🎁
You won’t have to manually write the d attribute yourself. 🎉
While it’s helpful to understand its role, in practice, you’ll rely on d3.js helper functions to generate paths for you.
These functions are all part of a d3 module called d3-shape. They follow a consistent pattern: taking your data and converting it into the appropriate path d string.
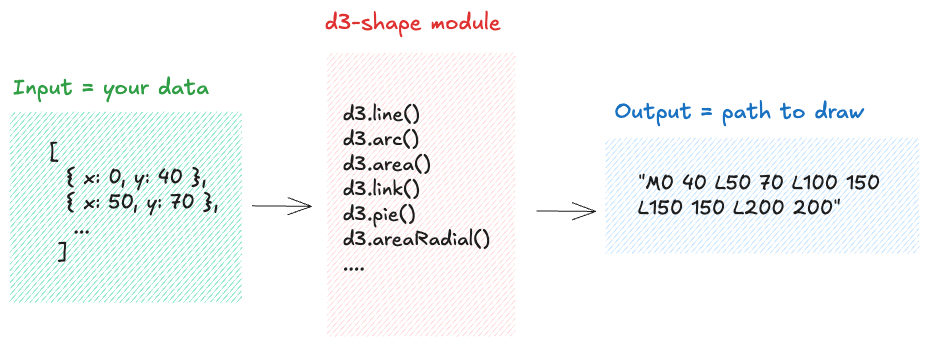
The d3-shape module provides functions that generate SVG paths from a dataset. It’s a core component of d3.js!
The d3-shape module is one of the most useful in d3.js! 💙
It’s also the focus of the next lesson.